Determining the most fertile days in your menstrual cycle is crucial whether you’re actively planning for that positive pregnancy test or simply interested in understanding your body’s reproductive patterns.
Here, we will delve into the different stages of the menstrual cycle, examine how to best utilize your fertile window, and equip you with the knowledge you need to optimize your chances of becoming pregnant.
The 4 Stages of the Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle is comprised of four different stages. While the length or number of days a particular stage will last can vary from woman to woman, the order of the stages is the same for everyone. The four stages of the menstrual cycle are:
#1. The Menstruation Phase
Menstruation is the first phase of the menstrual cycle and is also called a period. During a woman’s period, the lining of the uterus, called the endometrium, will be shed. Typically over the course of 3-5 days, menstrual blood flows from the uterus through the cervix and out of the body through the vagina.
Menstruation is controlled by the hormones estrogen and progesterone. Estrogen causes the lining of the uterus to thicken and prepare for pregnancy. Progesterone helps to maintain the thickened lining. If pregnancy does not occur, the levels of estrogen and progesterone drop, and the lining of the uterus begins to break down.
#2. The Follicular Phase
The second phase of the menstrual cycle is called the follicular phase. The follicular phase lasts a little more than a week on average. During this phase, a group of tiny egg-containing sacs, called follicles, start to grow in the ovaries.
One of these follicles will become the dominant follicle and later release an egg. The growth of the follicles is due to a release of FSH or follicle-stimulating hormone, which is produced by the pituitary gland near the brain. As the follicles grow, they produce more estrogen, which helps to rethicken the lining of your uterus that was shed during your last period.
#3. The Ovulation Phase
During a standard 28-day menstrual cycle, the third phase called ovulation begins on or around day 14. While the exact length of time a woman will ovulate varies from person to person, this phase typically lasts only one day, making it the shortest of the four phases.
When ovulating, one of the two ovaries will release a mature egg. A surge of LH or luteinizing hormone triggers the release of the egg. The ovulation phase of the menstrual cycle is when the likelihood of becoming pregnant due to unprotected sex is highest.
#4. The Luteal Phase
The fourth and final phase of the menstrual cycle is known as the luteal phase, which typically lasts about two weeks. During the luteal phase, the empty follicle left in the ovary after an egg has been released produces progesterone, which helps continue to thicken the lining of the uterus in preparation for pregnancy.
As the uterine lining thickens, the egg travels down the fallopian tube. If the egg is fertilized when ovulation occurs, it will implant in the now-thickened uterine lining. This attachment in the uterus is called implantation. The implantation window typically occurs about 6 to 10 days after ovulation.
If the egg is not fertilized, it will not implant, and the lining of the uterus will break down. The broken-down lining will be shed from the body during menstruation, starting the cycle over again.
The Likelihood of Conception During Each Menstrual Phase
While it is technically possible for women that are sexually active to become pregnant during every phase of the menstrual cycle, the likelihood of conception varies significantly for each.
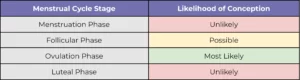
Source: Elsevier Inc.
The Likelihood of Conception By Age
The success rate for conception can be affected by many factors, with age being one of the most common. A woman’s ability to become pregnant often directly correlates with her age.
Women looking for more information on when they are most fertile should consider short-term windows of opportunity, like phases within their menstrual cycle, and long-term factors like age.
Typically, women in their 20s have a higher likelihood of conception compared to other age groups, as they often have uniform menstrual cycles and more healthy eggs. Normally, female fertility begins to decline after the age of 30. This decline in fertility continues as the years pass. When a woman is in her 40s, unassisted conception can be much more difficult.
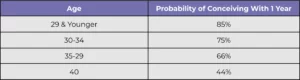
Source: Upsala Journal of Medical Sciences
Note that most metrics used when determining the likelihood of becoming pregnant are averages, and individual circumstances may vary. Some women experience fertility challenges as early as their 20s, while many women successfully conceive well into their 40s. Additionally, male fertility can also impact the likelihood of conceiving.
Does Having Sex After Ovulation Affect Implantation?
Having sexual intercourse after ovulation does not typically affect the process of embryo implantation. Once an egg is fertilized, it travels down the fallopian tube to the uterus, where it may implant into the uterine lining. This process is independent of sexual activity that occurs after ovulation, and is not disrupted by sexual intercourse during this time. In fact, having sex is typically safe at any point during pregnancy, unless your doctor tells you otherwise.
Can Fertility Treatments Help You Ovulate for Longer Periods of Time?
When a woman faces challenges involving her sexual health, consulting a fertility specialist can be very beneficial. These specialists can provide many different treatments. For example, they can administer medications to stimulate the ovaries, thereby potentially helping a woman to ovulate for longer periods of time.
Other treatments might involve in vitro fertilization (IVF), during which, an embryo transfer is performed to place a fertilized egg directly into the female reproductive tract. In some cases, these treatments may also lead to uterine contractions, which are a natural part of the process as the body prepares for a possible pregnancy.
Determining Your Baby’s Gender with Peekaboo
When you use Peekaboo™, you can determine your baby’s gender as early as six weeks gestation! The Peekaboo™ At-Home Early Gender Test is easy, affordable, and accurate. That’s why it’s the only early baby gender reveal test endorsed by the American Pregnancy Association.
Ready to discover your baby’s gender?
Get the Peekaboo At-Home Early Gender DNA Test, proven to be over 99% accurate, and discover your baby’s gender as early as 6 weeks from the comfort of home!


